A patient may develop acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome when chronic alcohol use is interrupted by hospital admission. Increasingly patients are being treated for alcohol withdrawal on general medical wards. In the gradually tapering regimen, patients receive a predetermined dose of medication that is gradually weaned over a few days. In the fixed dose regimen, patients received a specified dose of medication several times daily for 2 to 3 days. These 2 regimens can be given in either the inpatient or outpatient setting. A symptom-triggered regimen utilizes the patients symptoms, assessed at frequent intervals (i.e., every 1-2 hours), to help determine the dose and frequency of the medication.
It’s also essential to watch for subtle shifts in the patient’s status. It’s important for nurses to assess their patients’ alcohol intake upon admission. If patients indicate that they drink, ask for how many years, when they had their last drink, and what they typically drink and how much.
The principal investigators of the study request that you use the official version of the modified score here. It is the dedication of healthcare workers that will lead us through this crisis. Read our comprehensive protocols to protect patients from COVID-19.
Most patients who drink heavily and daily will have at least mild withdrawal when they stop drinking, e.g., with headache, nausea, tremors, diaphoresis, and anxiety. This usually starts about 12 hours after the last drink and lasts 4 to 5 days. Severe alcohol withdrawal are preventable if treated early, and are far easier to prevent than to treat. Early identification of problem drinking allows prevention or treatment of complications, including severe withdrawal. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force28 recommends screening patients for problem drinking through a careful history or standardized screening questionnaire.
Using The Ciwa
While chronic drinking affects all of these organs, the abrupt withdrawal of alcohol most immediately affects the brain. The brain balances and directs the activity of neurotransmitters, which carry signals to the peripheral nervous system and direct nearly every bodily function. For every neurotransmitter moving along a neuron carrying a signal, there must be a receptor in the receiving cell ready to accept that signal. The interaction between a neurotransmitter and its receptor initiates a series of biochemical events in the receiving cell.
However, it is important to keep in mind that at present, BZDs are the most effective and manageable drugs for the treatment of AWS. Topiramate is an anticonvulsant with several mechanisms of action. In particular, topiramate produces an increase in GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory activity and antagonizes AMPA and kainate glutamate receptors with a consequent reduction in DA release in the nucleus accumbens. It is able to modulate ionotropic channels, inhibiting L-type calcium channels, limiting the activity of voltage-dependent sodium channels and facilitating potassium conductance. All these effects are at the basis of topiramate’s ability to reduce the hyperactivity and resulting anxiety of AWS . More recently, other drugs have been investigated as treatments for AWS . The treatment of AWS requires the use of a long-acting drug as a substitutive agent to be gradually tapered off .
Alcohol Withdrawal In The Inpatient Setting
SMO has been approved in some European countries for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome and for relapse prevention and maintenance of abstinence. It is not approved for this indication in other countries, as its addictive properties limit its use . However, at therapeutic doses for the treatment of alcohol-dependent patients SMO abuse seems to be a relatively limited phenomenon . Valproic acid (400–500 mg tid) is able to produce a dose-dependent improvement of AWS symptoms , with a reduced incidence of seizures and a protection toward the worsening of AWS severity (anti-kindling effect).
- AWS is considered to be complicated if patients present with or develop alcohol withdrawal seizures, alcohol withdrawal delirium, or alcohol-induced psychotic disorder.
- Severe withdrawal symptoms can be quite serious and in rare situations, they can actually be fatal.
- Onset of withdrawal as the top chart details is usually 6-24 hours after the last intake although withdrawal can occur when the BAL is decreasing and it does not have to be zero.
- Baclofen has shown promise in the management of alcohol dependency in preclinical and clinical studies.
This phase should be aggressively treated, in order to reduce the risk of medical complications , reduce patient suffering and improve quality of life. The direct effect of these measures will be, in most of cases, a strong physician-patient relationship. The latter is necessary to improve patient’s disposition toward medical management and to start a long-term, multidisciplinary treatment of alcohol dependence. No study has shown a clear superiority of any agent over the others. The greater evidence exists for the long-acting agents , given their ability to produce a smoother withdrawal . The clinical effect is mediated by the drug per se, and by its active metabolites produced by phase I liver oxidation.
Is Your Patient In Alcohol Withdrawal? Don’t Expect Ciwa To Tell You
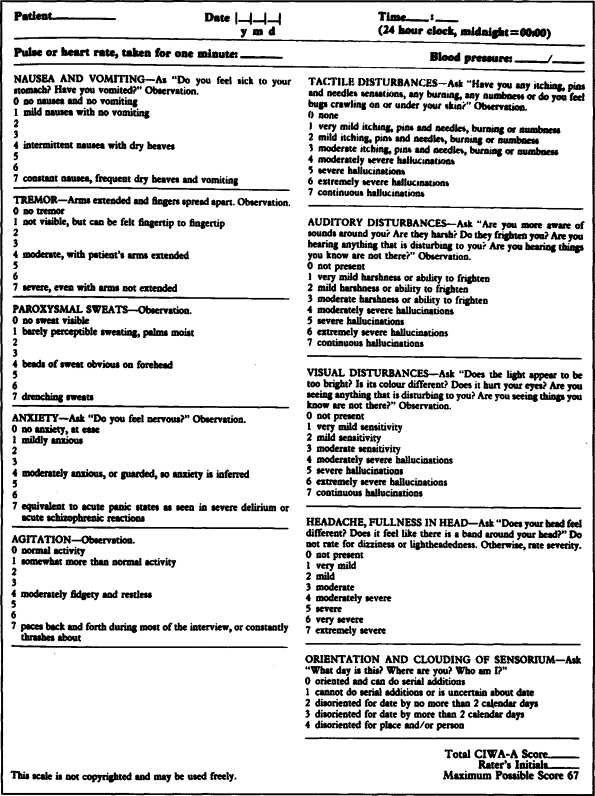
The scale contains 30 variables which are rated on an 8-point scale. Zero indicates the absence of a symptom, whilst 7 indicates the maximum severity. The 30-item scale was intended as a research tool and a shorter 11-item scale, the SSA, was produced for clinical use. — This paper reviews the literature on the use of rating scales within the treatment of the alcohol-withdrawal syndrome. A computer-assisted literature search identified trials of therapy for and rating scales used in alcohol-withdrawal states. There is a wide variation in symptom items included in these scales.
The signs or symptoms are not attributable to another medical condition and are not better explained by another mental disorder, including intoxication or withdrawal from another substance. Alcohol withdrawal delirium can often occur alongside another unrelated medical event, when an individual is admitted to hospital. For example, for liver failure, pneumonia, gastrointestinal bleeding, head trauma, hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalances, or postoperative care. Thus, it is always important to ask about alcohol during a hospital admission. During withdrawal, less than 10% will have severe autonomic hyperactivity, tremors, or alcohol withdrawal delirium.
Anti-epileptics are efficacious in preventing seizures as well as limiting the amount of benzodiazepines required for control of multiple symptoms of withdrawal. Carbamazepine has well-documented anticonvulsant activity and can prevent alcohol withdrawal seizures. The drug does not carry the same abuse potential as benzodiazepines and is less sedating. The major limitation of this drug is the likelihood of interaction with other medications.
The majority of people who drink excessively do not have an alcohol use disorder and/or aren’t dependent on alcohol. Severe withdrawal symptoms can be quite serious and in rare situations, they can actually be fatal. FPnotebook.com is a rapid access, point-of-care medical reference for primary care and emergency clinicians.
Your first step in getting the right answers when you need them. ClinicalKey is a clinical knowledge solution designed to help healthcare professionals and students find the right answers by providing in-depth, evidence-based knowledge – all from one resource. If your symptoms are more severe, you may need to stay in the hospital. This is so your doctor can monitor your condition and manage any complications. You may need to get fluids intravenously, or through your veins, to prevent dehydration and medications to help ease your symptoms. A high fever, hallucinations, and heart disturbances are all reasons to seek immediate help. The symptoms may worsen over 2 to 3 days, and some milder symptoms may persist for weeks in some people.
Adinoff B. Double-blind study of alprazolam, diazepam, clonidine, and the placebo in the alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Development of optimal treatment tactics for alcohol withdrawal. Impact of an alcohol withdrawal syndrome practice guideline on surgical patient outcomes. The early administration of a non-BZD agent together with gold-standard treatments represents a useful option to reduce the need for extra-dose BZD prescription (BZD-sparing drugs) and to start a medication with anti-craving properties . Beta-blockers (e.g. atenolol) could be used to treat hyperarousal symptoms in patients with coronary artery disease . However, given their effect on tremors, tachycardia and hypertension, these drugs could mask AWS symptoms and should be considered only in conjunction with BZDs in patients with persistent hypertension or tachycardia .
The mild-moderate form of AWS is often self-managed by patients or disappears within 2–7 days from the last drink , while the more severe AWS requires medical treatment . The identification and subsequent treatment of AWS is of paramount clinical importance, given that AWS is one of the causes of preventable morbidity and mortality . Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome may develop within 6–24 hours after the abrupt discontinuation or decrease of alcohol consumption. Symptoms can vary from autonomic hyperactivity and agitation to delirium tremens. The Recovery Village aims to improve the quality of life for people struggling with a substance use or mental health disorder with fact-based content about the nature of behavioral health conditions, treatment options and their related outcomes. We publish material that is researched, cited, edited and reviewed by licensed medical professionals.
Patient Follow
A score of greater than 15 is seen in patients with moderate to severe alcohol withdrawal. Patients with a score of greater than 15 or those who have a history of alcohol withdrawal seizures should be treated with medication upon presentation.
17 Small quantities of the withdrawal medication should be prescribed at each visit; thiamine and a multivitamin also should be prescribed. Because close monitoring is not available in ambulatory treatment, a fixed-schedule regimen should be used. Although the significance of kindling in alcohol withdrawal is debated, this phenomenon may be important in the selection of medications to treat withdrawal.